STI warning: ‘Serious’ STI on the rise in the UK and few have heard of it – key symptoms
Facts about sexually transmitted diseases
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
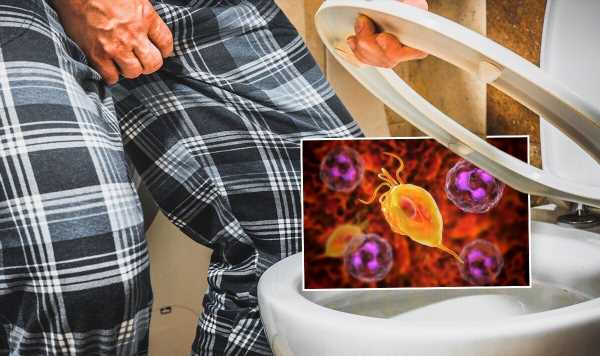
Britons are being urged to stay on high alert as there is a common STI on the rise in the UK and the consequences of catching it can be grave. “In my experience, while most people have heard of gonorrhoea, chlamydia and herpes, not many patients know about trichomoniasis (also known as trichomonas or ‘trich’),” said Doctor Sameer Sanghvi, a practising GP and Clinical Technology Lead at LloydsPharmacy Online Doctor.
Trichomoniasis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis (TV).
Despite a general lack of awareness, trichomoniasis is surprisingly rife in the UK and its effects can be ruinous, warned Doctor Sanghvi.
“Trich can be serious. Concerningly, it does appear that trich can make it easier for other STIs to enter the body,” explained the doc.
“In particular, trich puts you at greater risk of becoming infected with HIV (which can cause AIDS).”
According to the doc, the STI is particularly worrying for expectant mothers.
He explained: “If left untreated, trich can cause serious complications in pregnant women such as premature birth and low birthweight.”
According to Doctor Sanghvi, trichomoniasis has been in the news recently because new research suggests that it disproportionately affects women from ethnic minorities and deprived backgrounds.
How do you catch trichomoniasis?
The doc said: “The TV parasite is usually spread by having penetrative sex without a condom, although it can also be spread by sharing sex toys. It’s not thought to be passed on through oral or anal sex.”
DON’T MISS
Cliff Richard health: Star’s 3 tips for ‘healthy ageing’ [TIPS]
Sleep: The ‘Navy SEAL’ sleep hack to fall asleep in seconds [ADVICE]
Prostate cancer: 10 symptoms of a growing tumour [INSIGHT]
Like all STIs, you don’t have to have many sexual partners to catch trichomoniasis, notes the doc.
“Anybody who’s sexually active can catch it and pass it on.”
According to Doctor Sanghvi, the best way to avoid catching TV is to use a condom when having sex, covering any sex toys with a condom, and washing sex toys properly after use.
What are the symptoms of trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis symptoms in women include:
- Changes in colour, consistency, smell or quantity of vaginal discharge including an unpleasant fishy smell, a yellow-green colour or a thick, thin or frothy consistency
- Soreness, swelling and itching around the vagina or inner thighs
- Pain or discomfort when you pee or have sex.

Trichomoniasis symptoms in men include:
- Pain during when you pee or needing to pee more frequently
- Soreness, swelling and redness around the foreskin or head of the penis
- Thin, white discharge from the penis
- Pain during ejaculation.
“Symptoms of trichomoniasis usually develop within a month of infection,” explains Doctor Sanghvi.
He continued: “However, around half of people with trichomoniasis won’t present with any symptoms. This doesn’t mean they’re not able to pass the infection on to others which is why testing is paramount.”

Are chlamydia and trichomoniasis the same thing?
Doctor Sanghvi explained: “Although they share some of the same symptoms such as swelling and changes in discharge, chlamydia and trichomoniasis are not the same thing. To treat the infection effectively, it’s important to identify which infection you’ve got.”
How do you test for trichomoniasis?
If you notice any of the symptoms of trichomoniasis or have had sex with somebody who has tested positive for trichomoniasis, Doctor Sanghvi said it’s important to get tested.
Source: Read Full Article