Guideline issued for preventing SSI after major extremity trauma
In an evidence-based clinical practice guideline published by the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, recommendations are presented for the prevention of surgical site infection (SSI) after major extremity trauma.
Researchers evaluated the current best evidence associated with treatment to develop recommendations for prevention of SSI among adults after major extremity trauma. Fourteen strong and moderate-strength recommendations were developed.
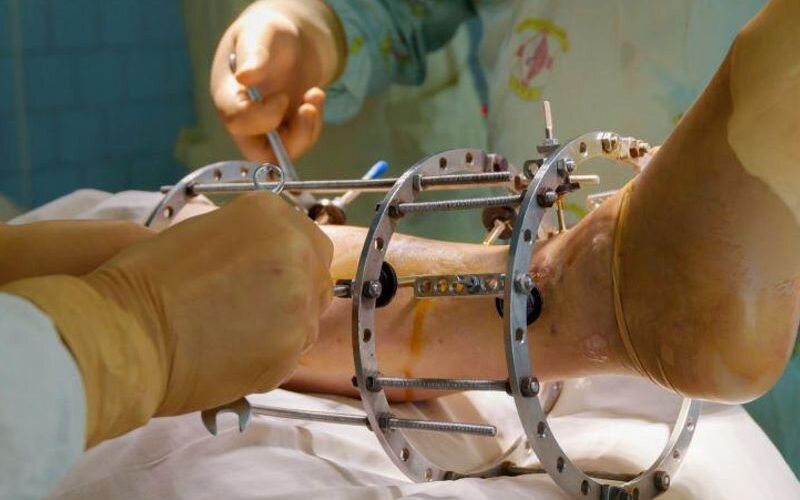
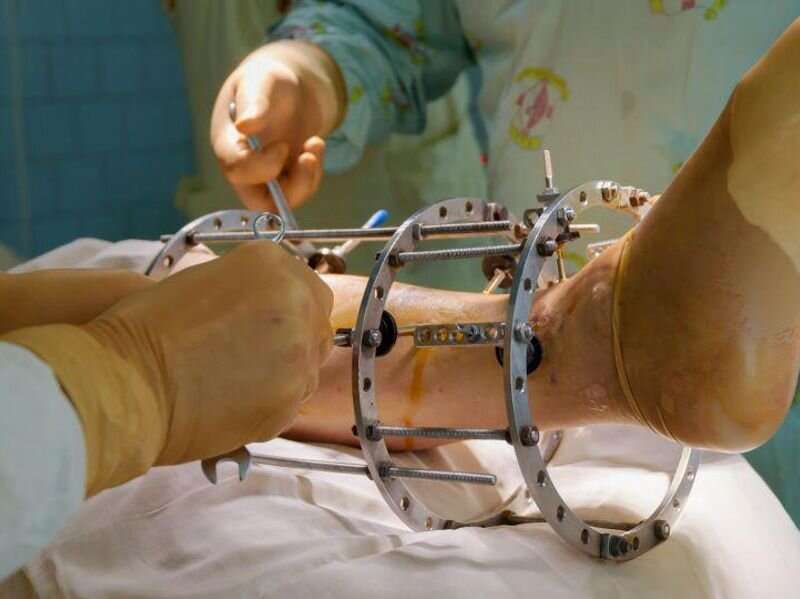
In the setting of open fracture in major extremity trauma, the authors suggest early delivery of antibiotics to reduce the risk for deep infection. In operative treatment of open fractures, preoperative antibiotics are suggested to prevent SSI. Patients with open fracture are suggested to be brought to the operating room for debridement and irrigation as soon as reasonable and ideally within 24 hours of injury. Antibiotic prophylaxis with systemic cefazolin or clindamycin is recommended for patients with major extremity trauma undergoing surgery, except for type III and possibly type II open fractures, for which Gram-negative coverage is preferred. Local antibiotic strategies may be beneficial for patients with major extremity trauma undergoing surgery. Irrigation with saline solution (without additives) is recommended for initial management of open wounds. Closing an open wound is recommended when it is feasible without any gross contamination. Silver-coated dressings are not suggested for improving outcomes or reducing pin site infections.
“We created this guideline as an educational tool to guide qualified physicians and clinicians in making treatment decisions that improve the quality and efficacy of care,” the authors write.
Source: Read Full Article